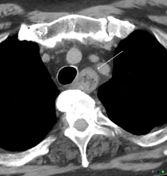
Esophageal food impaction
Updates to Synonym Attributes
Updates to Article Attributes
Body
was changed:
Oesophageal food impaction (or steakhouse syndrome) referes to a food bolus acutely obstructing the oesophagus.
Clinical presentation
The main symptom is usually of acute dysphagia.
Radiographic features
Depending on the composition of the the ingested content, the bolus may be visible on plain radiography. Small amounts of water-soluble isotonic contrast can be administered with fluoroscopic screening to evaluate the location of the bolus.
CT may be necessary if there is concern of perforation.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatments that are less invasive than endoscopy include effervescent crystals, coca-cola, glucagon, and muscle relaxants.
-<p><strong>Oesophageal food impaction</strong> (or <strong>steakhouse syndrome</strong>) referes to a food bolus acutely obstructing the oesophagus.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>The main symptom is usually of acute dysphagia.</p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><p>Depending on the composition of the ingested content, the bolus may be visible on plain radiography. Small amounts of water-soluble isotonic contrast can be administered with fluoroscopic screening to evaluate the location of the bolus. </p><p>CT may be necessary if there is concern of perforation. </p><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>Treatments that are less invasive than endoscopy include effervescent crystals, coca-cola, glucagon, and muscle relaxants.</p>- +<p><strong>Oesophageal food impaction</strong> (or <strong>steakhouse syndrome</strong>) referes to a food bolus acutely obstructing the oesophagus.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>The main symptom is usually of acute dysphagia.</p><h4>Radiographic features</h4><p>Depending on the composition of the ingested content, the bolus may be visible on plain radiography. Small amounts of water-soluble isotonic contrast can be administered with fluoroscopic screening to evaluate the location of the bolus. </p><p>CT may be necessary if there is concern of perforation. </p><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>Treatments that are less invasive than endoscopy include effervescent crystals, coca-cola, glucagon, and muscle relaxants.</p>
References changed:
- 1. Spinou E, Kubba H, Guse J, Johnston A. The Radiological Management of Oesophageal Food Bolus Obstruction Using a Gas-Forming Agent and Barium. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2003;30(1):103-5. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1016/s0385-8146(02)00054-8">doi:10.1016/s0385-8146(02)00054-8</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12589861">Pubmed</a>
- 2. Ginsberg G. Food Bolus Impaction. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2007;3(2):85-6. <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3099357">PMC3099357</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21960815">Pubmed</a>
- 3. Elango S, Palaniappan S, Lingam V, George L. Oesophageal Food Bolus Impaction. Singapore Med J. 1990;31(6):624-6. - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2281364">Pubmed</a>
Images Changes:
Image 1 CT (non-contrast) ( create )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.