Items tagged “lungs”
139 results found
Article
Subacute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
Subacute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (previously known as chronic necrotizing aspergillosis or semi-invasive aspergillosis) is subacute to chronic localized and indolent form of invasive aspergillosis. It is also sometimes grouped under the term chronic pulmonary aspergillosis.
Epidemiolog...
Article
Halo sign (chest)
The halo sign in chest imaging is a feature seen on lung window settings, ground glass opacity surrounding a pulmonary nodule or mass and represents hemorrhage. It is typically seen in angioinvasive aspergillosis.
Pathology
Histopathologically, it represents a focus of pulmonary infarction sur...
Case
Pulmonary arterial hypertension - primary

Published
23 Feb 2010
95% complete
X-ray
CT
Annotated image
Article
Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma, also known as malignant mesothelioma, is an aggressive malignant tumor of the mesothelium. Most tumors arise from the pleura, and so this article will focus on pleural mesothelioma.
Given the presence of the mesothelium in different parts of the body, mesothelioma can arise in var...
Case
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis

Published
24 Feb 2010
64% complete
X-ray
CT
Case
Lung abscess
Published
06 May 2020
83% complete
X-ray
CT
Case
Aspergilloma

Published
26 Feb 2010
45% complete
X-ray
CT
Article
Asbestos body
An asbestos body is a histological finding in interstitial lung disease that is suggestive of significant occupational asbestos exposure. They are usually identified following a parenchymal lung biopsy 3.
Macrophage ingestion of the asbestos fibers triggers a fibrogenic response via the release...
Case
Primary progressive pulmonary tuberculosis

Published
26 Feb 2010
85% complete
X-ray
Case
Asbestosis

Published
27 Feb 2010
50% complete
CT
Case
Secondary pulmonary lobules (gross pathology)

Published
27 Feb 2010
38% complete
Pathology
Case
Secondary pulmonary lobules (gross pathology)

Published
27 Feb 2010
29% complete
Pathology
Case
Secondary pulmonary lobule (illustration)

Published
27 Feb 2010
29% complete
Diagram
Article
Secondary pulmonary lobule
The secondary pulmonary lobule, also known as the pulmonary lobule, is considered the functional unit of the lung, and is key to HRCT terminology.
Terminology
The terminology used to describe the fundamental gas exchange units of the lung can be confusing. The inconsistent descriptions in part...
Article
Interlobular septa
The interlobular septa (singular: interlobular septum) are located between the secondary pulmonary lobules and are continuous with both the subpleural interstitium (peripheral connective tissue) and the peribronchovascular interstitium (axial connective tissue) as well as the more delicate intra...
Article
Intralobular septa
The intralobular septa (sing: septum) are delicate strands of connective tissue separating adjacent pulmonary acini and primary pulmonary lobules. They are continuous with the interlobular septa which surround and define the secondary pulmonary lobules.
See also
HRCT terminology
Article
Pulmonary acinus
The pulmonary acinus is an anatomical unit of lung supplied by a first order respiratory bronchiole, 4-8 mm in diameter. Each secondary pulmonary lobule usually contains 3-25 acini, and adjacent acini are separated by incomplete intralobular septa.
Clinical importance
The component respiratory...
Article
Centrilobular region
The centrilobular region, in context of the lungs and HRCT, refers to the central portion of the secondary pulmonary lobule, around the central pulmonary artery and bronchiole.
See also
HRCT terminology
Article
Pulmonary parenchymal bands
Parenchymal bands are a HRCT finding. They can be commonly encountered among patients with asbestosis.
They are typically over 2 cm in length (up to 5 cm), 1-3 mm thick and run through the lung parenchyma and usually extend from a visceral pleural surface 6. They are formed in a number of ways ...
Case
Normal anterior bronchus (annotated x-ray)
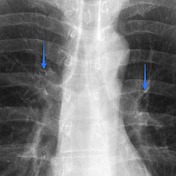
Published
02 Mar 2010
41% complete
X-ray







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.