Items tagged “mri physics”
13 results found
Article
Aliasing on MRI
Aliasing on MRI, also known as wrap-around, is a frequently encountered MRI artifact that occurs when the field of view (FOV) is smaller than the body part being imaged. The part of the body that lies beyond the edge of the FOV is projected onto the other side of the image 5.
This can be correc...
Article
Hunter's angle
Hunter's angle (HA) is a term coined from a neurosurgeon, C Hunter Shelden, at Huntington Medical Research Institutes. He placed his comb on the spectrum at approximately a 45° angle and connected several of the peaks. If the angle and peaks roughly corresponded to the 45° angle, the curve was c...
Article
Black boundary artifact
Black boundary artifact, also known as India ink artifact or type 2 chemical shift artifact, is an artificially-created black line located at fat-water interfaces such as those between muscle and fat. This results in a sharp delineation of the muscle-fat boundary lending the image an appearance ...
Article
Gradient coils
Gradient coils are used to produce deliberate variations in the main magnetic field (B0). There are three sets of gradient coils, one for each direction. The variation in the magnetic field permits localization of image slices as well as phase encoding and frequency encoding. The set of gradient...
Article
Radiofrequency coils
Radiofrequency coils (RF coils) are the "antennae" of the MRI system, broadcasting the RF signal to the patient and/or receiving the return signal. RF coils can be receive-only, in which case the body coil is used as a transmitter; or transmit and receive (transceiver).
Surface coils are the si...
Article
Resonance and radiofrequency
Protons in a magnetic field have a microscopic magnetization and act like tiny toy tops that wobble as they spin. The rate of the wobbling or precession is the resonance or Larmor frequency. In the magnetic field of an MRI scanner at room temperature, there is approximately the same number of pr...
Article
Superparamagnetism
Superparamagnetic materials consist of individual domains of elements that have ferromagnetic properties in bulk. Their magnetic susceptibility is between that of ferromagnetic and paramagnetic materials.
The figure illustrates the effect of a superparamagnetic material (grey circle) on the ma...
Case
Magnetic susceptibility artifact

Published
19 Apr 2013
73% complete
MRI
CT
Article
Dielectric effect artifact
Dielectric effect artifact is an MRI artifact encountered most often on body MRI with 3 T units.
Artifact
At 3 T, the radiofrequency (RF) wavelength measures 234 cm in air, and the speed and wavelength of the RF field is shortened to ~26 cm within the body as a result of dielectric effects. Ho...
Case
Dielectric effect artifact
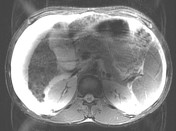
Published
23 Dec 2014
56% complete
MRI
Article
Ultrahigh field MRI
Ultrahigh field (UHF) magnetic resonance imaging refers to imaging done on any MRI scanner with a main magnetic field (B0) strength of 7 tesla or greater. Until recently purely a research tool, following the introduction of the first 7 T clinical scanner in 2017, there are now a slowly increasin...
Article
Fiber assignment by continuous tracking algorithm (FACT)
Fiber assignment by continuous tracking (FACT) algorithms are a commonly used deterministic post-processing algorithm for magnetic resonance tractography studies.
In these algorithms, axonal fiber bundles are reconstructed - voxel by voxel - following the direction of the main eigenvector. The ...
Case
Cross-excitation artifact (MRI)

Published
15 Jun 2021
77% complete
MRI







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.