Items tagged “orbit”
122 results found
Article
Abducens nerve
The abducens nerve is the sixth cranial nerve (CN VI). It is a motor nerve responsible for abduction of the eye (TA: nervus abducens or nervus cranialis VI). It courses from the abducens nucleus, located in the dorsal pons, up to the cavernous sinus, via a long cisternal segment that is prone to...
Article
Capillary hemangioma of the orbit
Capillary hemangiomas of the orbit, also known as strawberry hemangiomas, on account of its coloring, or orbital infantile hemangiomas, are the most common orbital tumors of infancy, and unlike orbital cavernous hemangiomas, they are neoplasms rather than vascular malformations.
Clinical presen...
Article
Idiopathic orbital inflammation
Idiopathic orbital inflammation, also known as orbital pseudotumor and non-specific orbital inflammation, is an idiopathic inflammatory condition that most commonly involves the extraocular muscles. Less commonly there is inflammatory change involving the uvea, sclera, lacrimal gland, and retrob...
Article
Phthisis bulbi
Phthisis bulbi, also known as end-stage eye, is an atrophic scarred and disorganized non-functioning globe that may result from a variety of severe ocular insults.
Epidemiology
In general, phthisis bulbi involves elderly patients, usually 65-85 years of age 7. Children and adolescents are onl...
Article
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastomas are the most common intraocular neoplasm found in childhood and with modern treatment modalities, are, in most cases, curable.
On imaging, they are generally characterized by a heterogeneous retinal mass with calcifications, necrotic components and increased vascularization on D...
Case
Caroticocavernous fistula (indirect)

Published
18 Jul 2008
65% complete
CT
DSA (angiography)
Case
Orbital metastases: breast cancer

Published
08 Oct 2008
59% complete
CT
Article
Orbital mass
An orbital mass carries a wide differential.
Differential diagnosis
tumors
lymphoma
metastasis
lacrimal gland or duct tumors
rhabdomyosarcoma of the orbit
retinoblastoma
optic nerve meningioma
optic nerve glioma
schwannoma (of trigeminal or other cranial nerves except optic)
neurofibr...
Article
Ophthalmic artery
The ophthalmic artery is a branch of the supraclinoid (C6) segment of the internal carotid artery.
Gross anatomy
Origin
The ophthalmic artery arises medial to the anterior clinoid process as the internal carotid artery exits the cavernous sinus. It originates from the antero- or supero-medial...
Case
Orbital varix

Published
27 Oct 2008
74% complete
CT
Article
Orbital venous varix
Orbital venous varix (plural: varices) is an uncommon vascular malformation that is composed of enlarged single or multiple tubular venous channels within the orbit with direct communication to the systemic venous system.
Terminology
Orbital venous varices are divided into primary and seconda...
Case
Thyroid orbitopathy
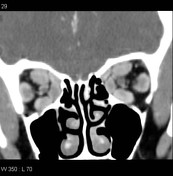
Published
16 Dec 2008
71% complete
CT
Case
Enophthalmos due to anorexia nervosa
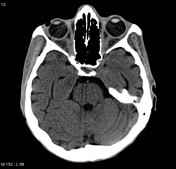
Published
02 Jan 2009
65% complete
CT
Case
Orbital cavernous hemangioma - extra conal

Published
06 Jan 2009
77% complete
MRI
Case
Ruptured globe

Published
06 Jan 2009
68% complete
CT
Case
Orbital abscess - lacrimal gland

Published
27 Jan 2009
56% complete
CT
Case
Multiple myeloma - orbit

Published
15 Apr 2009
80% complete
CT
Article
Trilateral retinoblastoma
Trilateral retinoblastoma refers to the combination of retinoblastoma (usually bilateral) and pineoblastoma. This relationship highlights the close relationship between these highly aggressive small round blue cell tumors.
It affects only a minority of patients with retinoblastoma (1.5-5%) and ...
Article
Optic pathway glioma
Optic pathway gliomas are relatively uncommon tumors, with a variable clinical course and usually seen in the setting of neurofibromatosis type I (NF1). Histologically the majority are pilocytic astrocytomas.
They are characterized by imaging by an enlarged optic nerve seen either on CT or MRI....
Article
Tram-track sign (orbit)
Tram-track sign refers to the parallel thickening and enhancement around the optic nerve, and is most frequently seen in the setting of optic nerve meningioma. It may, however, also be seen in 1:
orbital pseudotumor
perioptic neuritis
orbital sarcoidosis
orbital leukemia
orbital lymphoma
o...







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.