Items tagged “physics”
132 results found
Case
Stair step artifact (CT)

Published
13 Feb 2014
94% complete
CT
Article
Kilovoltage peak
Kilovoltage peak (kVp) is the peak potential applied to the x-ray tube, which accelerates electrons from the cathode to the anode in radiography or computed tomography. Tube voltage, in turn, determines the quantity and quality of the photons generated. An increase in kVp extends and intensifies...
Case
Static electricity

Published
14 Jul 2014
79% complete
X-ray
Case
Thermoluminescent dosimeter badge

Published
23 Jul 2014
41% complete
Photo
Article
Compton effect
Compton effect or Compton scatter is one of principle forms of photon interaction. It is the main cause of scattered radiation in a material. It occurs due to the interaction of the photon (x-ray or gamma) with free electrons (unattached to atoms) or loosely bound valence shell (outer shell) ele...
Case
Time gain compensation - diagram

Published
10 Aug 2014
41% complete
Diagram
Article
Speed displacement artifact
Speed displacement artifact, also known as propagation velocity artifact, is a gray scale ultrasound finding that can be identified as an area of focal discontinuity and displacement of an echo deeper than that its actual position in an imaged structure. Depth determination by an ultrasound mach...
Article
Entrance phosphor
The entrance phosphor (or input phosphor) is a component of the image intensifier in fluoroscopic systems that converts the energy from x-rays into light photons. It is composed of a fluorescent material such as cesium iodide activated with sodium (CsI:Na) and coats the entrance surface of the i...
Case
Anisotropy

Published
30 Oct 2014
91% complete
Ultrasound
Article
Linear attenuation coefficient
Linear attenuation coefficient (µ) is a constant that describes the fraction of attenuated incident photons in a monoenergetic beam per unit thickness of a material 1. It includes all possible interactions including coherent scatter, Compton scatter and photoelectric effect 1. Its complement is ...
Article
Young's modulus
Young's modulus is a relationship between elasticity, strain, and stress:
elasticity x (change in length / original length) = (force / area)
put another way, this is
elasticity x (strain) = stress
or
elasticity = stress / strain
Elasticity is measured in kilopascals (kPa).
This relationsh...
Article
Strain elastography
Strain elastography (also known as tissue strain elastography/static elastography/compression elastography) is a developing form of ultrasound that assesses tissues' macroscopic structure through the strain modulus. This is different from normal B-mode grayscale ultrasound which characterizes a ...
Article
Shear wave elastography
Shear wave elastography is a developing variation of ultrasound imaging.
The concept is similar to strain elastography, but instead of using transducer pressure to compare a shift in an ultrasound A-line (thereby measuring changes in strain), a higher intensity pulse is transmitted to produce s...
Article
Acoustic impedance
Acoustic impedance (Z) is a physical property of tissue. It describes how much resistance an ultrasound beam encounters as it passes through a tissue.
Acoustic impedance depends on:
the physical density of the tissue (d, in kg/m3)
the velocity of the soundwave transmitted through the tissue m...
Article
Decibel
The decibel (dB) is a unit that measures the relative difference between two sound intensities. The relationship is logarithmic:
dB = 10 log (I2 / I1)
dB = relative intensity of the sounds
I1 = intensity of sound 1
I2 = intensity of sound 2
Informally, decibel is a unit of "loudness", which...
Article
Hormesis
Hormesis is a controversial concept in toxicology. The proposed concept is that very tiny amounts of a toxin may potentially have beneficial biological effects, rather than deleterious effects ,2.
In the context of radiology it refers to a proposed modification to the linear no-threshold model ...
Article
Ernst angle
The Ernst angle is the flip angle that maximizes signal in T1-weighted sequences that have a short repetition time (TR).
When the TR is very short, the best flip angle to maximize signal can be quite small. Choosing the Ernst angle in this setting can increase signal by several fold. However, i...
Article
Dynamic nuclear polarization
Dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) is a phenomenon by which polarization is transferred from a polarizing agent to a biological tracer, enhancing the nuclear energy difference and thereby increasing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) dramatically.
Case
X-ray tube diagram
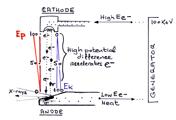
Published
28 Apr 2015
35% complete
Diagram
Case
Computed tomography equation

Published
28 Apr 2015
32% complete
Diagram







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.