Hypertrophic pachymeningitis
Disclosures
- updated 4 Feb 2023:
Nothing to disclose
Updates to Article Attributes
Body
was changed:
Hypertrophic pachymeningitis is a condition where there is localised or diffuse inflammatory thickening of the dura. On imaging, it presents as a localised, multiple, or diffuse enhancing dural thickening commonly forming mass-like lesions.
Clinical presentation
The clinical presentation may be varied 7. Common clinical features include headache and cranial nerve palsies 7.
Pathology
Aetiology
It can result from a number of causes which include 5-7:
- idiopathic
- infective
- inflammatory
- other
- Rosai-Dorfman disease
- haemodialysis
- mucopolysaccharidoses
Radiographic features
MRI
- localised, or less often, diffuse dural thickening
- may uncommonly depict mass-like thickening, termed tumefactive hypertrophic pachymeningitis 1
Signal characteristics:
- T1: thickened areas are hypointense to brain parenchyma 6
- T1 C+ (Gd): dural enhancement
- T2: thickened areas are hypointense to brain parenchyma 6
Treatment and prognosis
Management depends on the underlying cause, and includes immunosuppression in idiopathic cases 7.
Differential diagnosis
General imaging differential considerations include:
- meningeal metastases
- meningeal involvement with CNS lymphoma
- multiple meningiomas including lymphoplasmacyte-rich meningioma
- intracranial involvement with Erdheim Chester disease
-<p><strong>Hypertrophic </strong><strong>pachymeningitis</strong> is a condition where there is localised or diffuse inflammatory thickening of the <a href="/articles/dura-mater">dura</a>. On imaging, it presents as a localised, multiple, or diffuse enhancing dural thickening commonly forming mass-like lesions. </p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>The clinical presentation may be varied <sup>7</sup>. Common clinical features include headache and cranial nerve palsies <sup>7</sup>.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><h5>Aetiology</h5><p>It can result from a number of causes which include <sup>5-7</sup>:</p><ul>-<li>idiopathic</li>-<li>infective<ul>-<li><a href="/articles/neurosyphilis">neurosyphilis</a></li>-<li>-<a href="/articles/tuberculosis-intracranial-manifestations">CNS tuberculosis</a>: <a href="/articles/tuberculous-pachymeningitis">tuberculous pachymeningitis</a>-</li>-<li><a href="/articles/cns-cryptococcosis-2">CNS cryptococcosis</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/bacterial-meningitis">bacterial meningitis</a></li>-</ul>-</li>-<li>inflammatory<ul>-<li><a href="/articles/igg4-related-hypertrophic-pachymeningitis-1">IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis">granulomatosis with polyangiitis</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/neurosarcoidosis">neurosarcoidosis</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/polyarteritis-nodosa-1">polyarteritis nodosa</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/rheumatoid-arthritis">rheumatoid arthritis</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/relapsing-polychondritis">relapsing polychondritis</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/behcet-disease-2">Behçet disease</a></li>-</ul>-</li>-<li>other<ul>-<li><a href="/articles/rosai-dorfman-disease">Rosai-Dorfman disease</a></li>-<li>haemodialysis</li>-<li><a href="/articles/mucopolysaccharidoses-2">mucopolysaccharidoses</a></li>-</ul>-</li>-</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>MRI</h5><ul>-<li>localised, or less often, diffuse dural thickening</li>-<li>may uncommonly depict mass-like thickening, termed tumefactive hypertrophic pachymeningitis <sup>1</sup>-</li>-</ul><p>Signal characteristics:</p><ul>-<li>-<strong>T1:</strong> thickened areas are hypointense to brain parenchyma <sup>6</sup>-</li>-<li>-<strong>T1 C+ (Gd):</strong> <a href="/articles/dural-enhancement">dural enhancement</a>-</li>-<li>-<strong>T2: </strong>thickened areas are hypointense to brain parenchyma <sup>6</sup>-</li>-</ul><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>Management depends on the underlying cause, and includes immunosuppression in idiopathic cases <sup>7</sup>.</p><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><p>General imaging differential considerations include:</p><ul>-<li><a href="/articles/leptomeningeal-metastases">meningeal metastases</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/cns-lymphoma-1">meningeal involvement with CNS lymphoma</a></li>-<li>-<a href="/articles/meningioma">multiple meningiomas</a> including <a href="/articles/lymphoplasmacyte-rich-meningioma-2">lymphoplasmacyte-rich meningioma</a>-</li>-<li>intracranial involvement with <a href="/articles/erdheim-chester-disease">Erdheim Chester disease</a>-</li>- +<p><strong>Hypertrophic </strong><strong>pachymeningitis</strong> is a condition where there is localised or diffuse inflammatory thickening of the <a href="/articles/dura-mater">dura</a>. On imaging, it presents as a localised, multiple, or diffuse enhancing dural thickening commonly forming mass-like lesions. </p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>The clinical presentation may be varied <sup>7</sup>. Common clinical features include headache and cranial nerve palsies <sup>7</sup>.</p><h4>Pathology</h4><h5>Aetiology</h5><p>It can result from a number of causes which include <sup>5-7</sup>:</p><ul>
- +<li>idiopathic</li>
- +<li>infective<ul>
- +<li><a href="/articles/neurosyphilis">neurosyphilis</a></li>
- +<li>
- +<a href="/articles/tuberculosis-intracranial-manifestations">CNS tuberculosis</a>: <a href="/articles/tuberculous-pachymeningitis">tuberculous pachymeningitis</a>
- +</li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/cns-cryptococcosis-2">CNS cryptococcosis</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/bacterial-meningitis">bacterial meningitis</a></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>inflammatory<ul>
- +<li><a href="/articles/igg4-related-hypertrophic-pachymeningitis-1">IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis">granulomatosis with polyangiitis</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/neurosarcoidosis">neurosarcoidosis</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/polyarteritis-nodosa-1">polyarteritis nodosa</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/rheumatoid-arthritis">rheumatoid arthritis</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/relapsing-polychondritis">relapsing polychondritis</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/behcet-disease-2">Behçet disease</a></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +<li>other<ul>
- +<li><a href="/articles/rosai-dorfman-disease">Rosai-Dorfman disease</a></li>
- +<li>haemodialysis</li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/mucopolysaccharidoses-2">mucopolysaccharidoses</a></li>
- +</ul>
- +</li>
- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>MRI</h5><ul>
- +<li>localised, or less often, diffuse dural thickening</li>
- +<li>may uncommonly depict mass-like thickening, termed tumefactive hypertrophic pachymeningitis <sup>1</sup>
- +</li>
- +</ul><p>Signal characteristics:</p><ul>
- +<li>
- +<strong>T1:</strong> thickened areas are hypointense to brain parenchyma <sup>6</sup>
- +</li>
- +<li>
- +<strong>T1 C+ (Gd):</strong> <a href="/articles/dural-enhancement">dural enhancement</a>
- +</li>
- +<li>
- +<strong>T2: </strong>thickened areas are hypointense to brain parenchyma <sup>6</sup>
- +</li>
- +</ul><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>Management depends on the underlying cause, and includes immunosuppression in idiopathic cases <sup>7</sup>.</p><h4>Differential diagnosis</h4><p>General imaging differential considerations include:</p><ul>
- +<li><a href="/articles/leptomeningeal-metastases">meningeal metastases</a></li>
- +<li><a href="/articles/cns-lymphoma-1">meningeal involvement with CNS lymphoma</a></li>
- +<li>
- +<a href="/articles/meningioma">multiple meningiomas</a> including <a href="/articles/lymphoplasmacyte-rich-meningioma-2">lymphoplasmacyte-rich meningioma</a>
- +</li>
- +<li>intracranial involvement with <a href="/articles/erdheim-chester-disease">Erdheim Chester disease</a>
- +</li>
Images Changes:
Image 5 MRI (T1 C+) ( create )
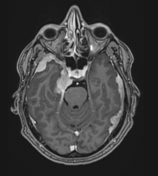
Caption
was added:
Case 3
Position
was set to
5.







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.