Sinonasal polyposis
Updates to Article Attributes
Sinonasal polyposis refers to a specific pattern of chronic sinusitis.
Chronic inflammatory sinusitis is commonly classified into five patterns namely ostiomeatal complex (OMC) , infundibular , sphenoethmoidal recess ,sinonasal polyposis and sporadic patterns.
This classification usually determines the type of surgery to perform.
Clinical presentation
Clinical symptoms can include
- progressive nasal stuffiness
- rhinorrhea
- facial pain
- headache
- anosmia
Radiographic features:
CT
Features include
Extensiveextensive mucosal polyps are occupying and obliterating the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses.Thethe inferior nasal meatus occasionally spared.Associatedassociated benign bone remodeling or erosion may be seen.Concurrentconcurrent fungal infectioniscan be common.- truncation of middle turbinate 4
- enlargement of infundibula
- bony attenuation of the ethmoid trabeculae and nasal septum
- opacified ethmoid sinuses with convex lateral walls and air-fluid levels.
-<p><strong>Sinonasal polyposis </strong>refers to a specific pattern of <a title="Chronic sinusitis" href="/articles/chronic-sinusitis">chronic sinusitis</a>.</p><p>Chronic inflammatory <a title="Sinusitis - chronic" href="/articles/sinusitis-chronic">sinusitis </a>is commonly classified into five patterns namely ostiomeatal complex (OMC) , infundibular , sphenoethmoidal recess ,sinonasal polyposis and sporadic patterns.</p><p>This classification usually determines the type of surgery to perform.</p><h6>Radiographic features:</h6><ul>-<li><p>Extensive mucosal polyps are occupying and obliterating the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses.</p></li>-<li><p>The inferior nasal meatus occasionally spared.</p></li>-<li><p>Associated benign bone remodeling or erosion may be seen.</p></li>-<li>-<p>Concurrent<a title="fungal infection" href="/articles/fungal-infection"> fungal infection</a> is common.</p>-<p> </p>- +<p><strong>Sinonasal polyposis </strong>refers to a specific pattern of <a href="/articles/chronic-sinusitis">chronic sinusitis</a>.</p><p>Chronic inflammatory <a href="/articles/sinusitis-chronic">sinusitis </a>is commonly classified into five patterns namely ostiomeatal complex (OMC) , infundibular , sphenoethmoidal recess ,sinonasal polyposis and sporadic patterns.</p><p>This classification usually determines the type of surgery to perform.</p><h4>Clinical presentation</h4><p>Clinical symptoms can include</p><ul>
- +<li>progressive nasal stuffiness</li>
- +<li>rhinorrhea</li>
- +<li>facial pain</li>
- +<li>headache</li>
- +<li>anosmia</li>
- +</ul><h4>Radiographic features</h4><h5>CT</h5><p>Features include</p><ul>
- +<li>extensive mucosal polyps are occupying and obliterating the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses.</li>
- +<li>the inferior nasal meatus occasionally spared.</li>
- +<li>associated benign bone remodeling or erosion may be seen.</li>
- +<li>concurrent<a href="/articles/fungal-infection"> fungal infection</a> can be common.</li>
- +<li>truncation of middle turbinate <sup>4</sup>
- +<li>enlargement of infundibula</li>
- +<li>bony attenuation of the ethmoid trabeculae and nasal septum</li>
- +<li>opacified ethmoid sinuses with convex lateral walls and air-fluid levels.</li>
References changed:
- 2. Hussain S, Woo E, Connor S. Sinonasal Imaging. Imaging. 2013;22(1):20110001. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1259/imaging.20110001">doi:10.1259/imaging.20110001</a>
- 4. Liang E, Lam W, Woo J, Van Hasselt C, Metreweli C. Another CT Sign of Sinonasal Polyposis: Truncation of the Bony Middle Turbinate. Eur Radiol. 1996;6(4):553-6. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182492">doi:10.1007/BF00182492</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8798041">Pubmed</a>
- 5. Drutman J, Babbel R, Harnsberger H, Sonkens J, Braby D. Sinonasal Polyposis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1991;12(6):561-74. - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1786179">Pubmed</a>
- 1. Heinz Stammberger, Wolfgang Kopp, Gino Hasler. Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. (1991) ISBN: 9780941158961 - <a href="http://books.google.com/books?vid=ISBN9780941158961">Google Books</a>
- 3. Drutman J, Harnsberger H, Babbel R, Sonkens J, Braby D. Sinonasal Polyposis: Investigation by Direct Coronal CT. Neuroradiology. 1994;36(6):469-72. <a href="https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00593686">doi:10.1007/BF00593686</a> - <a href="https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7991094">Pubmed</a>
- Hussain S, Woo EK, Connor SEJ. Sinonasal imaging. Imaging 2013;22:20110001
- Stammberger H. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Philadelphia, PA: BC Decker; 1991.
Image 1 CT (non-contrast) ( create )

Image 2 CT (bone window) ( update )
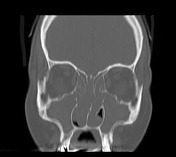
Image 3 CT (Soft tissue) ( create )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.