Trochanteric fracture
Updates to Article Attributes
Trochanteric fracture is a fracture involving the greater and lesser/or lesser trochanters of the femur.
Classification
These areFractures in these region can be classified into:as
- intertrochanteric
- subtrochanteric
- greater trochanteric avulsion fracture
- lesser trochanteric avulsion fracture
Intertrochanteric fracture
They are subdivided as per number of fragments into:
- two-part linear intertrochanteric fracture stable
- three-part with comminution of lesser trochanter or greater trochanter
- four-part with comminution of both trochanters
- multi-part with comminution of both trochanters and intertrochanteric region
The Boyd and Griffin classificationfurtherclassified it basis of involvement involvement of subtrochanteric region:
- type I linear intertrochanteric
- type II with comminution of trochanteric region
- type III with comminution associated with subtrochanteric component
- type IV oblique fracture of shaft with extension into subtrochanteric region
Subtrochonteric fracture
The Fielding classification of subtrochanteric fractures is based on the level of the subtrochanteric region through which the fracture extends. :
- type I: at the level of the lesser trochanter (most common)
- type II: within the region 2.5 cm below the lesser trochanter
- type III: within the region 2.5 cm to 5 cm below the lesser trochanter (least common)
The Zickel classification (modified from Fielding) of subtrochanteric fractures takes into consideration the level and obliquity of the fracture line as well as the presence or absence of comminution.
- type I short oblique
- linear
- comminuted
- type II long oblique
- linear
- comminuted
- type III transverse
- high level
- low level
Treatment and prognosis
Subtrochanteric fractures generally have a good prognosis due to the good supply of blood and adequate collateral circulation to this region of the femur with low incidence of avascular necrosis and non-union. Postoperative infection, however, is a potentially serious compilation.
See also
-<p><strong>Trochanteric fracture</strong> is a fracture involving the greater and lesser trochanters of the femur.</p><h4>Classification</h4><p>These are classified into:</p><ul>- +<p><strong>Trochanteric fracture</strong> is a fracture involving the greater and/or lesser trochanters of the <a title="Femur" href="/articles/femur">femur</a>.</p><h4>Classification</h4><p>Fractures in these region can be classified as</p><ul>
- +<li>greater trochanteric avulsion fracture</li>
- +<li>lesser trochanteric avulsion fracture</li>
-</ul><p><strong>Boyd and Griffin </strong>further<strong> </strong>classified it on the basis of involvement of subtrochanteric region:</p><ul>- +</ul><p>The <strong>Boyd and Griffin classification</strong> is based on the involvement of subtrochanteric region:</p><ul>
-</ul><h5>Subtrochonteric fracture</h5><p><strong>Fielding</strong> classification of subtrochanteric fractures is based on the level of the subtrochanteric region through which the fracture extends. </p><ul>- +</ul><h5>Subtrochonteric fracture</h5><p>The <strong>Fielding</strong> <strong>classification</strong> of subtrochanteric fractures is based on the level of the subtrochanteric region through which the fracture extends:</p><ul>
-</ul><p>The <strong>Zickel</strong> classification (modified from Fielding) of subtrochanteric fractures takes into consideration the level and obliquity of the fracture line as well as the presence or absence of comminution.</p><ul>- +</ul><p>The <strong>Zickel</strong> <strong>classification</strong> (modified from Fielding) of subtrochanteric fractures takes into consideration the level and obliquity of the fracture line as well as the presence or absence of comminution.</p><ul>
-</ul><p>Subtrochanteric fractures generally have a good prognosis due to the good supply of blood and adequate collateral circulation to this region of the femur with low incidence of avascular necrosis and non-union. Postoperative infection, however, is a potentially serious compilation.</p><h4>See also</h4><ul>-<li><a href="/articles/femoral-neck-fracture">femoral neck fracture</a></li>-<li><a href="/articles/subcapital-fracture">subcapital fracture</a></li>-</ul>- +</ul><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><p>Subtrochanteric fractures generally have a good prognosis due to the good supply of blood and adequate collateral circulation to this region of the femur with low incidence of avascular necrosis and non-union. Postoperative infection, however, is a potentially serious compilation.</p>
References changed:
- 2. Ahn J, Bernstein J. Fractures in brief: intertrochanteric hip fractures. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010;468 (5): 1450-2. <a href="http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11999-010-1263-2">doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1263-2</a> - <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2853662">Free text at pubmed</a> - <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20195807">Pubmed citation</a><span class="auto"></span>
Image ( destroy )
Image 1 Diagram ( update )

Image 3 X-ray (Frontal) ( create )
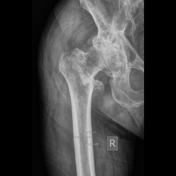
Image 5 X-ray (Frontal) ( create )

Image 7 X-ray (Oblique) ( create )

Image 8 X-ray (Frontal) ( create )

Image 9 X-ray (Frontal) ( create )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.