Urinary bladder diverticulum
Updates to Article Attributes
Bladder diverticulum are outpouchings from the bladder wall, whereby mucosa herniates through the bladder wall. They may be solitary or multiple in nature and can very considerably in size.
Epidemiology
There are two peaks - one at 10 years and the other at 60-70 years 2.
Pathology
Diverticulae may be congenital (primary) or acquired (secondary) and a a range of causes of urinary bladder diverticula are described.
Acquired diverticula are more common, usually occurring the context of a trabeculated bladder, resulting from chronic bladder outlet obstruction.
Radiographic appearance
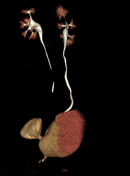
Diverticula are often an incidental finding on imaging investigations, including ultrasound, CT, MRI and IVU.
Treatment and prognosis
Complications
They may be associated with a range of complications due to stasis and low-grade infection including:
- intra diverticulartransitional cell carcinoma 1-10%
- bladder stones
- bladder rupture
-<p><strong>Bladder diverticulum</strong> are outpouchings from the bladder wall, whereby mucosa herniates through the bladder wall. They may be solitary or multiple in nature and can very considerably in size.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>There are two peaks - one at 10 years and the other at 60-70 years <sup>2</sup>. </p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>Diverticulae may be congenital (primary) or acquired (secondary) and a range of <a href="/articles/causes-of-urinary-bladder-diverticulae-1">causes of urinary bladder diverticula</a> are described. </p><p>Acquired diverticula are more common, usually occurring the context of a trabeculated bladder, resulting from chronic bladder outlet obstruction.</p><h5>Radiographic appearance</h5><p>Diverticula are often an incidental finding on imaging investigations, including ultrasound, CT, MRI and IVU.</p><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><h5>Complications</h5><p>They may be associated with a range of complications due to stasis and low-grade infection including:</p><ul>-<li>intra diverticular <a href="/articles/transitional-cell-carcinoma-of-the-urinary-tract">transitional cell carcinoma</a> 1-10%</li>- +<p><strong>Bladder diverticulum</strong> are outpouchings from the bladder wall, whereby mucosa herniates through the bladder wall. They may be solitary or multiple in nature and can very considerably in size.</p><h4>Epidemiology</h4><p>There are two peaks - one at 10 years and the other at 60-70 years <sup>2</sup>. </p><h4>Pathology</h4><p>Diverticulae may be congenital (primary) or acquired (secondary) and a range of <a href="/articles/causes-of-urinary-bladder-diverticulae-1">causes of urinary bladder diverticula</a> are described. </p><p>Acquired diverticula are more common, usually occurring the context of a trabeculated bladder, resulting from chronic bladder outlet obstruction.</p><h5>Radiographic appearance</h5><p>Diverticula are often an incidental finding on imaging investigations, including ultrasound, CT, MRI and IVU.</p><h4>Treatment and prognosis</h4><h5>Complications</h5><p>They may be associated with a range of complications due to stasis and low-grade infection including:</p><ul>
- +<li>intra diverticular <a href="/articles/transitional-cell-carcinoma-of-the-urinary-tract">transitional cell carcinoma</a> 1-10%</li>
Image 5 CT (VR) ( create )







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.