Central pontine myelinolysis
Updates to Case Attributes
Central pontine myelinolysis" was (CPM) was first termed in 1959 by Adams to describe a symmetric, demyelinating focus prominent in the central pons.The original patient population included only chronic alcoholics.This condition, however, has also been found in the malnourished, transplant recipients, or chronically debilitated patients,in particular, those in whom electrolyte abnormalities include hyponatremia that is rapidly over-corrected. Symptoms
Symptoms of CPM include tetraplegia, pseudobulbar palsy, and acute changes in mental status leading to coma or death without intervention. Similar histologic symmetric lesions were later identified in extrapontine locations, including the white matter of the cerebellum, thalamus, globus pallidus, putamen, and lateral geniculate body, a condition termed “extrapontineextrapontine myelinolysis”.
Today, the term osmotic demyelination syndrome is preferred to reflect both pontine and extrapontine involvement.
-<p>"<a title="Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM)" href="/articles/central-pontine-myelinolysis">Central pontine myelinolysis</a>" was first termed in 1959 by Adams to describe a symmetric, demyelinating focus prominent in the central pons.The original patient population included only chronic alcoholics.This condition, however, has also been found in the malnourished, transplant recipients, or chronically debilitated patients,in particular, those in whom electrolyte abnormalities include hyponatremia that is rapidly over-corrected. Symptoms of CPM include tetraplegia, pseudobulbar palsy, and acute changes in mental status leading to coma or death without intervention. Similar histologic symmetric lesions were later identified in extrapontine locations, including the white matter of the cerebellum, thalamus, globus pallidus, putamen, and lateral geniculate body, a condition termed “extrapontine myelinolysis”</p>- +<p><a href="/articles/osmotic-demyelination-syndrome">Central pontine myelinolysis</a> (CPM) was first termed in 1959 by Adams to describe a symmetric, demyelinating focus prominent in the central pons.The original patient population included only chronic alcoholics.This condition, however, has also been found in the malnourished, transplant recipients, or chronically debilitated patients,in particular, those in whom electrolyte abnormalities include hyponatremia that is rapidly over-corrected. </p><p>Symptoms of CPM include tetraplegia, <a title="Pseudobulbar palsy" href="/articles/pseudobulbar-palsy">pseudobulbar palsy</a>, and acute changes in mental status leading to coma or death without intervention. Similar histologic symmetric lesions were later identified in extrapontine locations, including the white matter of the cerebellum, thalamus, globus pallidus, putamen, and lateral geniculate body, a condition termed <a title="Extrapontine myelinolysis (EPM)" href="/articles/extrapontine-myelinolysis-1">extrapontine myelinolysis</a>. </p><p>Today, the term <a title="Osmotic demyelination syndrome" href="/articles/osmotic-demyelination-syndrome">osmotic demyelination syndrome</a> is preferred to reflect both pontine and extrapontine involvement. </p>
Updates to Study Attributes
A symmetric andand well-delimited lesion is seen located at the central portion of the pons withhypersignalT2-weightedhyposignal onlow signal on T1 images. This lesion spares the peripheral fibers.
Image MRI (FLAIR) ( update )

Image MRI (T2) ( update )
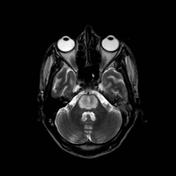
Image MRI (T1) ( update )
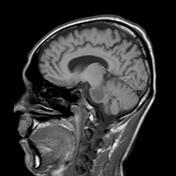
Image 1 MRI (T1) ( update )

Image 2 MRI (FLAIR) ( update )

Image 3 MRI (T2) ( update )








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.